Cannabinoid receptors, once thought to be exclusive to humans, have now been discovered in various other mammals, including dogs. These receptors play a crucial role in the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which regulates a multitude of physiological processes. Understanding the presence and function of cannabinoid receptors in dogs can shed light on the potential effects of cannabinoids, such as CBD, on their health and well-being.
Cannabinoid Receptors in Dogs
Cannabinoid receptors are specialized proteins found throughout the body, including in the brains and nervous systems of humans and animals. These receptors are part of the endocannabinoid system, a complex network involved in regulating various physiological functions such as mood, appetite, pain sensation, and immune response.
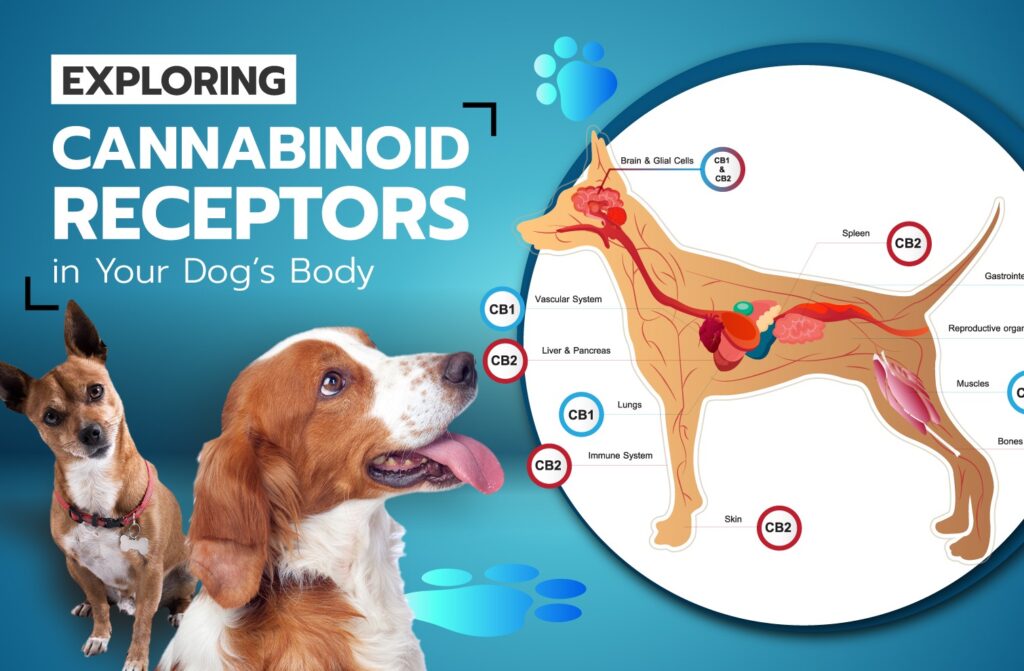
In the context of dogs, research has shown that they possess cannabinoid receptors, specifically CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are primarily located in the brain and central nervous system, where they influence functions like pain perception, appetite, and mood regulation. CB2 receptors are predominantly found in peripheral tissues, including the immune system, where they play a role in modulating inflammation and immune responses.
The presence of these cannabinoid receptors in dogs suggests that they, like humans, have an endocannabinoid system that helps maintain balance within their bodies. This discovery has significant implications for understanding how cannabinoids, such as CBD (cannabidiol), may interact with dogs’ physiology.
When cannabinoids like CBD interact with these receptors, they can potentially produce various therapeutic effects in dogs. These effects may include pain relief, reduction of inflammation, and alleviation of anxiety or stress. This has led to growing interest in using cannabinoid-based products for managing a range of health conditions in dogs, from arthritis to seizures.
However, it’s important to approach the use of cannabinoids in dogs cautiously. While there is promising research indicating their potential benefits, further studies are needed to fully understand their safety, efficacy, and appropriate dosing for different conditions. Pet owners should always consult with veterinarians before administering any cannabinoid products to ensure the well-being of their furry companions.
Functions and Implications of cannabinoid receptors in dogs
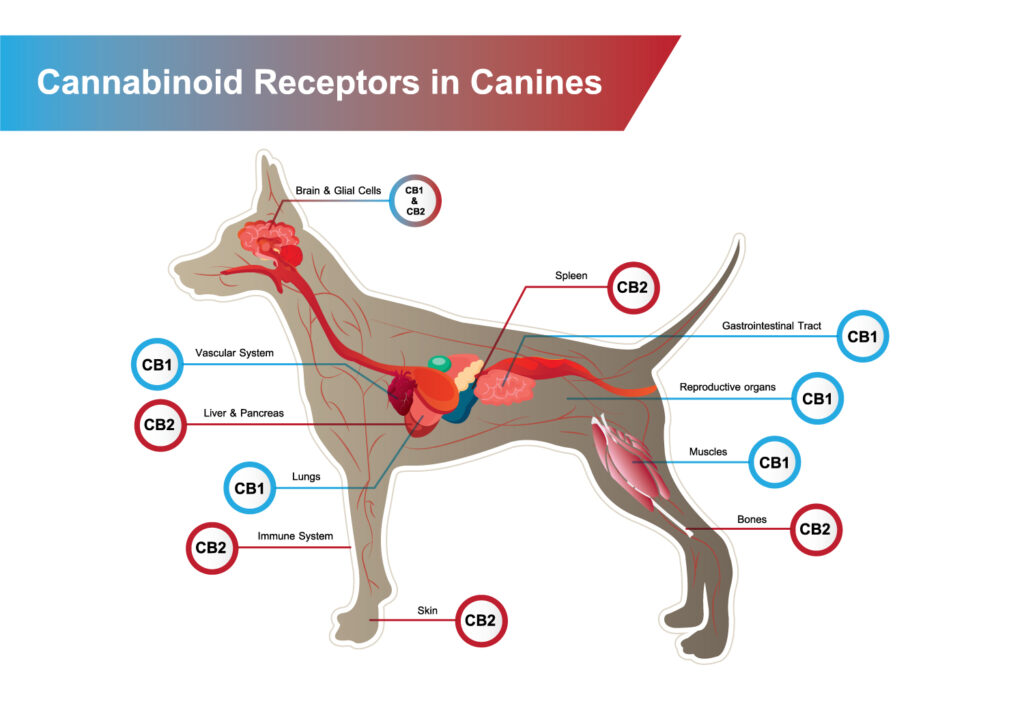
- Regulation of Physiological Functions: Cannabinoid receptors, particularly CB1 and CB2 receptors, play a pivotal role in regulating various physiological functions in dogs. These functions include pain perception, appetite regulation, mood modulation, immune response, and inflammation control.
- Endocannabinoid System (ECS): The presence of cannabinoid receptors suggests that dogs have an endocannabinoid system similar to humans. The ECS is a complex network of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids that work together to maintain balance, or homeostasis, within the body. Activation of cannabinoid receptors by endocannabinoids or external cannabinoids can help regulate these physiological processes.
- Therapeutic Potential: Understanding the presence of cannabinoid receptors in dogs opens up possibilities for using cannabinoids, such as CBD, for therapeutic purposes. CBD, in particular, has shown promise in managing various health conditions in dogs, including pain, inflammation, anxiety, seizures, and gastrointestinal issues.
- Pain Management: Cannabinoid receptors, especially CB1 receptors, are involved in modulating pain perception in dogs. Activating these receptors with cannabinoids like CBD may help alleviate pain associated with conditions such as arthritis, injuries, or surgical procedures.
- Inflammation Control: CB2 receptors, primarily located in peripheral tissues and the immune system, are crucial for regulating inflammation and immune responses. CBD’s interaction with these receptors can potentially reduce inflammation associated with conditions like allergies, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory bowel disease in dogs.
- Anxiety and Stress Reduction: CB1 receptors in the brain are involved in regulating mood and anxiety levels. By targeting these receptors, cannabinoids like CBD may help reduce anxiety and stress in dogs, making it useful for managing separation anxiety, noise phobias, or general anxiety disorders.
- Safety Considerations: While cannabinoids offer therapeutic potential for dogs, it’s essential to approach their use with caution. Further research is needed to determine optimal dosages, potential side effects, and long-term safety profiles. Pet owners should consult with veterinarians before incorporating cannabinoid products into their pets‘ wellness regimens.
In summary, the discovery of cannabinoid receptors in dogs opens up new avenues for exploring the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids in veterinary medicine. Understanding how cannabinoids interact with these receptors can help develop safe and effective treatments for various health conditions in dogs, improving their overall well-being and quality of life.
potential applications of cannabinoid receptors in dogs
- Pain Management: Cannabinoid receptors, especially CB1 receptors found in the brain and nervous system of dogs, play a crucial role in modulating pain perception. Activation of these receptors by cannabinoids like CBD can potentially alleviate pain associated with various conditions such as arthritis, injuries, surgical procedures, or chronic pain syndromes.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: CB2 receptors, primarily located in peripheral tissues and the immune system of dogs, are involved in regulating inflammation. By targeting these receptors, cannabinoids like CBD may help reduce inflammation associated with conditions such as allergies, autoimmune diseases, inflammatory bowel disease, or joint disorders like arthritis.
- Anxiety and Stress Relief: CB1 receptors in the brain are involved in regulating mood, anxiety, and stress levels. Cannabinoids such as CBD may interact with these receptors to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety and stress in dogs. This can be beneficial for managing separation anxiety, noise phobias, fear of fireworks, or general anxiety disorders.
- Seizure Management: Some research suggests that cannabinoids, particularly CBD, may have anticonvulsant properties that could help in managing seizures in dogs, including epilepsy. While further studies are needed to fully understand the mechanisms and effectiveness, anecdotal evidence and initial research show promise in this area.
- Gastrointestinal Health: Cannabinoid receptors are also present in the gastrointestinal tract of dogs, where they may influence gut motility, inflammation, and digestive processes. CBD has been explored for its potential to alleviate symptoms associated with gastrointestinal disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease, nausea, vomiting, and appetite stimulation.
- Supportive Care in Cancer: While not a primary treatment for cancer, cannabinoids like CBD may offer supportive care for dogs undergoing cancer treatment. CBD’s anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anti-nausea properties could help manage symptoms associated with cancer or side effects of chemotherapy, improving the quality of life for affected dogs.
- General Wellness and Homeostasis: Cannabinoid receptors play a role in maintaining overall homeostasis within the body. By interacting with these receptors, cannabinoids may promote general wellness and balance in dogs, supporting their overall health and vitality.
It’s important to note that while there is growing interest in using cannabinoids for various health conditions in dogs, further research, clinical trials, and veterinary guidance are essential to ensure safe and effective use. Pet owners should always consult with veterinarians before starting any cannabinoid-based treatments for their furry companions.
Conclusion: The discovery of cannabinoid receptors in dogs underscores the intricate similarities between mammalian species and highlights the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids in veterinary medicine. As research in this field continues to evolve, so too will our understanding of how cannabinoids can be effectively utilized to improve the health and well-being of our canine companions.
